We developed an interactive benchmark of 26 visual CAPTCHAs, totaling 2600 challenges to compare Halligan against state-of-the-art CAPTCHA solvers. We selected CAPTCHAs based on availability (as paid commercial services), popularity (identified from top 1 million websites), and AI-completeness (has visual puzzles requiring AGI for human-level performance).
Comparison Study
Results
Halligan successfully solved 1,577 out of 2,600 challenges, achieving a solve rate of 60.7%. Halligan, being a generalist agent, is capable of solving all types of CAPTCHA in the benchmark without few-shot examples, pre-training or fine-tuning. As long as visual CAPTCHAs are converted into abstract representations that VLM agents can both understand and manipulate, they can be solved with reasonable success. Hover for more details, see the next section for explanation on failure cases.
Failure Cases

(1) Close: 280 out of 1023 (27.4%) solutions were nearly correct but fell short. The solution is just outside the tolerance range or very similar to the ground truth. Examples include a single incorrect character in textbased CAPTCHAs, sliding or dragging solutions a few pixels off, and quantification tasks (e.g., object counting) that are off by one.
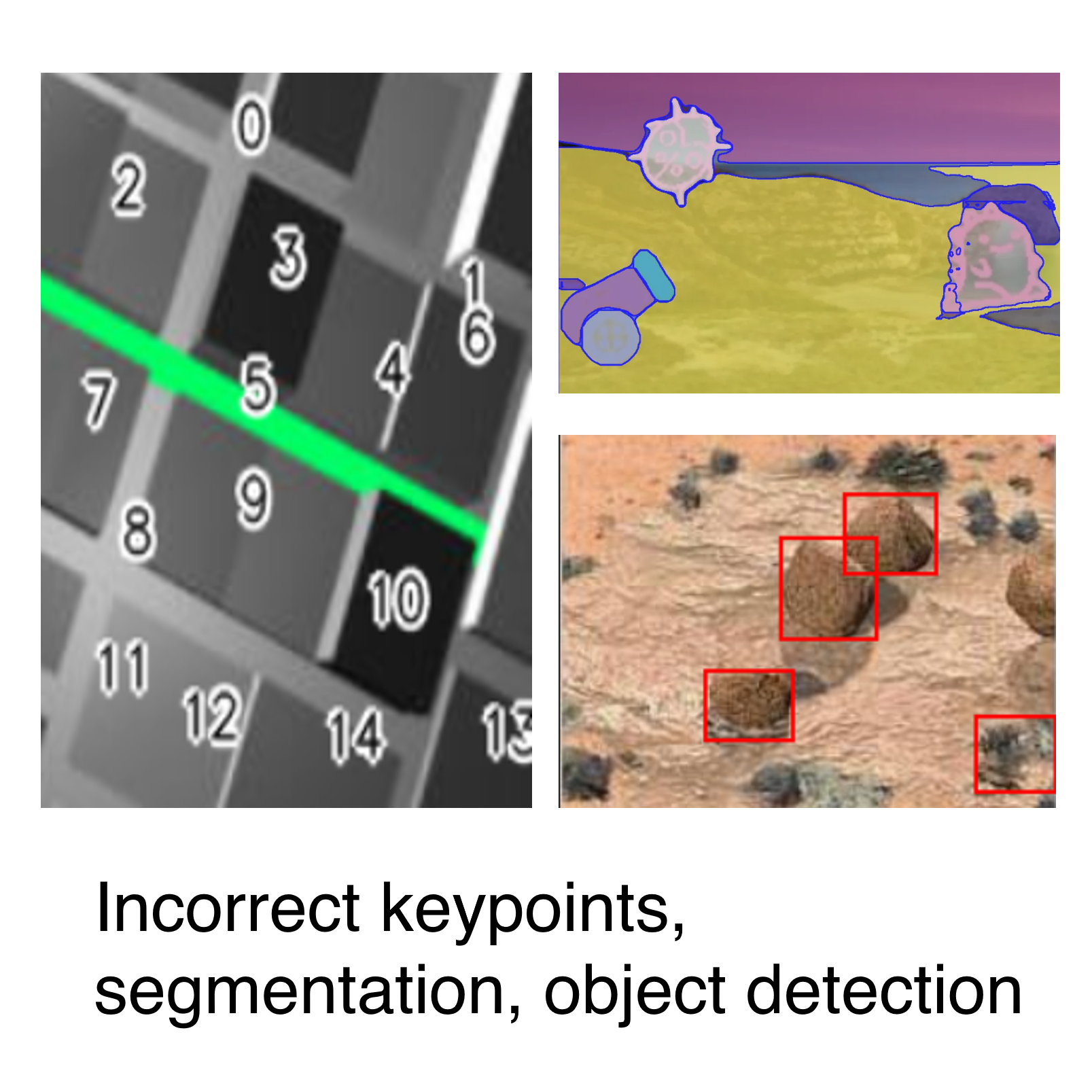
(2) External Tools: 218 out of 1023 (21.3%) failed due to limitations in large vision models. They are caused by bad outputs from mark() and focus() (i.e., using object detection model), leading to faulty reasoning downstream.

(3) Solution Comparison: 488 out of 1023 (47.7%) were due to suboptimal solution during search that arises from ask(), rank(), and compare(), which use gpt-4o for visual question answering.

(4) Search Objective Construction: 7 out of 1023 (3.6%) were the result of misunderstanding the task instructions.
Solve Times
After abstracting a visual CAPTCHA and framing it as a search problem, the median time to compose a solution is 4.5 seconds, while the median execution time is 6.3 seconds. The figure below shows a box plot of execution times grouped by CAPTCHA type. Notably, different CAPTCHA types from the same service exhibit high variability (e.g., arkose, geeTest). Additionally, solve times vary within individual CAPTCHA types, with some challenges showing greater variance. Halligan's performance is comparable to human solving times (ranging from 3.1 to 42 seconds) and ad hoc bots (0.016 to 17.5 seconds). Hover for more details.